|
| November 13, 2012 | Volume 08 Issue 42 |
Motion Control News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Overhung load adaptors provide load support and contamination protection
 Overhung load adaptors (OHLA) provide both overhung radial and axial load support to protect electrified mobile equipment motors from heavy application loads, extending the lifetime of the motor and alleviating the cost of downtime both from maintenance costs and loss of production. They seal out dirt, grime, and other contaminants too. Zero-Max OHLAs are available in an extensive offering of standard models (including Extra-Duty options) for typical applications or customized designs.
Overhung load adaptors (OHLA) provide both overhung radial and axial load support to protect electrified mobile equipment motors from heavy application loads, extending the lifetime of the motor and alleviating the cost of downtime both from maintenance costs and loss of production. They seal out dirt, grime, and other contaminants too. Zero-Max OHLAs are available in an extensive offering of standard models (including Extra-Duty options) for typical applications or customized designs.
Learn more.
Why choose electric for linear actuators?
 Tolomatic has been delivering a new type of linear motion technology that is giving hydraulics a run for its money. Learn the benefits of electric linear motion systems, the iceberg principle showing total cost of ownership, critical parameters of sizing, and conversion tips.
Tolomatic has been delivering a new type of linear motion technology that is giving hydraulics a run for its money. Learn the benefits of electric linear motion systems, the iceberg principle showing total cost of ownership, critical parameters of sizing, and conversion tips.
Get this informative e-book. (No registration required)
New AC hypoid inverter-duty gearmotors
 Bodine Electric Company introduces 12 new AC inverter-duty hypoid hollow shaft gearmotors. These type 42R-25H2 and 42R-30H3 drives combine an all-new AC inverter-duty, 230/460-VAC motor with two hypoid gearheads. When used with an AC inverter (VFD) control, these units deliver maintenance-free and reliable high-torque output. They are ideal for conveyors, gates, packaging, and other industrial automation equipment that demands both high torque and low power consumption from the driving gearmotor.
Bodine Electric Company introduces 12 new AC inverter-duty hypoid hollow shaft gearmotors. These type 42R-25H2 and 42R-30H3 drives combine an all-new AC inverter-duty, 230/460-VAC motor with two hypoid gearheads. When used with an AC inverter (VFD) control, these units deliver maintenance-free and reliable high-torque output. They are ideal for conveyors, gates, packaging, and other industrial automation equipment that demands both high torque and low power consumption from the driving gearmotor.
Learn more.
Next-gen warehouse automation: Siemens, Universal Robots, and Zivid partner up
 Universal Robots, Siemens, and Zivid have created a new solution combining UR's cobot arms with Siemens' SIMATIC Robot Pick AI software and Zivid's 3D sensors to create a deep-learning picking solution for warehouse automation and intra-logistics fulfillment. It works regardless of object shape, size, opacity, or transparency and is a significant leap in solving the complex challenges faced by the logistics and e-commerce sectors.
Universal Robots, Siemens, and Zivid have created a new solution combining UR's cobot arms with Siemens' SIMATIC Robot Pick AI software and Zivid's 3D sensors to create a deep-learning picking solution for warehouse automation and intra-logistics fulfillment. It works regardless of object shape, size, opacity, or transparency and is a significant leap in solving the complex challenges faced by the logistics and e-commerce sectors.
Read the full article.
Innovative DuoDrive gear and motor unit is UL/CSA certified
 The DuoDrive integrated gear unit and motor from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS is a compact, high-efficiency
solution engineered for users in the fields of intralogistics, pharmaceutical, and the food and beverage industries. This drive combines a IE5+ synchronous motor and single-stage helical gear unit into one compact housing with a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. It has a system efficiency up to 92% and is available in two case sizes with a power range of 0.5 to 4.0 hp.
The DuoDrive integrated gear unit and motor from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS is a compact, high-efficiency
solution engineered for users in the fields of intralogistics, pharmaceutical, and the food and beverage industries. This drive combines a IE5+ synchronous motor and single-stage helical gear unit into one compact housing with a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. It has a system efficiency up to 92% and is available in two case sizes with a power range of 0.5 to 4.0 hp.
Learn more.
BLDC flat motor with high output torque and speed reduction
 Portescap's 60ECF brushless DC slotted flat motor is the newest frame size to join its flat motor portfolio. This 60-mm BLDC motor features a 38.2-mm body length and an outer-rotor slotted configuration with an open-body design, allowing it to deliver improved heat management in a compact package. Combined with Portescap gearheads, it delivers extremely high output torque and speed reduction. Available in both sensored and sensorless options. A great choice for applications such as electric grippers and exoskeletons, eVTOLs, and surgical robots.
Portescap's 60ECF brushless DC slotted flat motor is the newest frame size to join its flat motor portfolio. This 60-mm BLDC motor features a 38.2-mm body length and an outer-rotor slotted configuration with an open-body design, allowing it to deliver improved heat management in a compact package. Combined with Portescap gearheads, it delivers extremely high output torque and speed reduction. Available in both sensored and sensorless options. A great choice for applications such as electric grippers and exoskeletons, eVTOLs, and surgical robots.
Learn more and view all the specs.
Application story: Complete gearbox and coupling assembly for actuator system
 Learn how GAM engineers not only sized and selected the appropriate gear reducers and couplings required to drive two ball screws in unison using a single motor, but how they also designed the mounting adapters necessary to complete the system. One-stop shopping eliminated unnecessary components and resulted in a 15% reduction in system cost.
Learn how GAM engineers not only sized and selected the appropriate gear reducers and couplings required to drive two ball screws in unison using a single motor, but how they also designed the mounting adapters necessary to complete the system. One-stop shopping eliminated unnecessary components and resulted in a 15% reduction in system cost.
Read this informative GAM blog.
Next-gen motor for pump and fan applications
 The next evolution of the award-winning Aircore EC motor from Infinitum is a high-efficiency system designed to power commercial and industrial applications such as HVAC fans, pumps, and data centers with less energy consumption, reduced emissions, and reduced waste. It features an integrated variable frequency drive and delivers upward of 93% system efficiency, as well as class-leading power and torque density in a low-footprint package that is 20% lighter than the previous version. Four sizes available.
The next evolution of the award-winning Aircore EC motor from Infinitum is a high-efficiency system designed to power commercial and industrial applications such as HVAC fans, pumps, and data centers with less energy consumption, reduced emissions, and reduced waste. It features an integrated variable frequency drive and delivers upward of 93% system efficiency, as well as class-leading power and torque density in a low-footprint package that is 20% lighter than the previous version. Four sizes available.
Learn more.
Telescoping linear actuators for space-constrained applications
 Rollon's new TLS telescoping linear actuators enable long stroke lengths with minimal closed lengths, which is especially good for applications with minimal vertical clearance. These actuators integrate seamlessly into multi-axis systems and are available in two- or three-stage versions. Equipped with a built-in automated lubrication system, the TLS Series features a synchronized drive system, requiring only a single motor to achieve motion. Four sizes (100, 230, 280, and 360) with up to 3,000-mm stroke length.
Rollon's new TLS telescoping linear actuators enable long stroke lengths with minimal closed lengths, which is especially good for applications with minimal vertical clearance. These actuators integrate seamlessly into multi-axis systems and are available in two- or three-stage versions. Equipped with a built-in automated lubrication system, the TLS Series features a synchronized drive system, requiring only a single motor to achieve motion. Four sizes (100, 230, 280, and 360) with up to 3,000-mm stroke length.
Learn more.
Competitively priced long-stroke parallel gripper
 The DHPL from Festo is a new generation of pneumatic long-stroke grippers that offers a host of advantages for high-load and high-torque applications. It is interchangeable with competitive long-stroke grippers and provides the added benefits of lighter weight, higher precision, and no maintenance. It is ideal for gripping larger items, including stacking boxes, gripping shaped parts, and keeping bags open. It has high repetition accuracy due to three rugged guide rods and a rack-and-pinion design.
The DHPL from Festo is a new generation of pneumatic long-stroke grippers that offers a host of advantages for high-load and high-torque applications. It is interchangeable with competitive long-stroke grippers and provides the added benefits of lighter weight, higher precision, and no maintenance. It is ideal for gripping larger items, including stacking boxes, gripping shaped parts, and keeping bags open. It has high repetition accuracy due to three rugged guide rods and a rack-and-pinion design.
Learn more.
Extend your range of motion: Controllers for mini motors
 FAULHABER has added another extremely compact Motion Controller without housing to its product range. The new MC3603 controller is ideal for integration in equipment manufacturing and medical tech applications. With 36 V and 3 A (peak current 9 A), it covers the power range up to 100 W and is suitable for DC motors with encoder, brushless drives, or linear motors.
FAULHABER has added another extremely compact Motion Controller without housing to its product range. The new MC3603 controller is ideal for integration in equipment manufacturing and medical tech applications. With 36 V and 3 A (peak current 9 A), it covers the power range up to 100 W and is suitable for DC motors with encoder, brushless drives, or linear motors.
Learn more.
When is a frameless brushless DC motor the right choice?
 Frameless BLDC motors fit easily into small, compact machines that require high precision, high torque, and high efficiency, such as robotic applications where a mix of low weight and inertia is critical. Learn from the experts at SDP/SI how these motors can replace heavier, less efficient hydraulic components by decreasing operating and maintenance costs. These motors are also more environmentally friendly than others.
Frameless BLDC motors fit easily into small, compact machines that require high precision, high torque, and high efficiency, such as robotic applications where a mix of low weight and inertia is critical. Learn from the experts at SDP/SI how these motors can replace heavier, less efficient hydraulic components by decreasing operating and maintenance costs. These motors are also more environmentally friendly than others.
View the video.
Tiny and smart: Step motor with closed-loop control
 Nanotec's new PD1-C step motor features an integrated controller and absolute encoder with closed-loop control. With a flange size of merely 28 mm (NEMA 11), this compact motor reaches a max holding torque of 18 Ncm and a peak current of 3 A. Three motor versions are available: IP20 protection, IP65 protection, and a motor with open housing that can be modified with custom connectors. Ideal for applications with space constraints, effectively reducing both wiring complexity and installation costs.
Nanotec's new PD1-C step motor features an integrated controller and absolute encoder with closed-loop control. With a flange size of merely 28 mm (NEMA 11), this compact motor reaches a max holding torque of 18 Ncm and a peak current of 3 A. Three motor versions are available: IP20 protection, IP65 protection, and a motor with open housing that can be modified with custom connectors. Ideal for applications with space constraints, effectively reducing both wiring complexity and installation costs.
Learn more.
Closed loop steppers drive new motion control applications
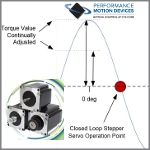 According to the motion experts at Performance Motion Devices, when it comes to step motors, the drive technique called closed loop stepper is making everything old new again and driving a burst of interest in the use of two-phase step motors. It's "winning back machine designers who may have relegated step motors to the category of low cost but low performance."
According to the motion experts at Performance Motion Devices, when it comes to step motors, the drive technique called closed loop stepper is making everything old new again and driving a burst of interest in the use of two-phase step motors. It's "winning back machine designers who may have relegated step motors to the category of low cost but low performance."
Read this informative Performance Motion Devices article.
Intelligent compact drives with extended fieldbus options
 The intelligent PD6 compact drives from Nanotec are now available with Profinet and EtherNet/IP. They combine motor, controller, and encoder in a space-saving package. With its 80-mm flange and a rated power of 942 W, the PD6-EB is the most powerful brushless DC motor of this product family. The stepper motor version has an 86-mm flange (NEMA 34) and a holding torque up to 10 Nm. Features include acceleration feed forward and jerk-limited ramps. Reduced installation time and wiring make the PD6 series a highly profitable choice for machine tools, packaging machines, or conveyor belts.
The intelligent PD6 compact drives from Nanotec are now available with Profinet and EtherNet/IP. They combine motor, controller, and encoder in a space-saving package. With its 80-mm flange and a rated power of 942 W, the PD6-EB is the most powerful brushless DC motor of this product family. The stepper motor version has an 86-mm flange (NEMA 34) and a holding torque up to 10 Nm. Features include acceleration feed forward and jerk-limited ramps. Reduced installation time and wiring make the PD6 series a highly profitable choice for machine tools, packaging machines, or conveyor belts.
Learn more.
Drill, baby, drill: Astrobotic unveils working prototype of lunar water-prospecting robot
Astrobotic Technology has completed assembly of a full-size prototype of Polaris, a solar-powered robot that will search for potentially rich deposits of water ice at the moon's poles. The first of its kind, Polaris can accommodate a drill to bore 1 m into the lunar surface and is being designed to operate in lunar regions characterized by dark, long shadows and a sun that hugs the horizon.

The 5 1/2-ft-tall Polaris aims to drill for water ice on the moon.
Astrobotic, a Carnegie Mellon University spinoff that develops robotics technology for planetary missions, is developing Polaris for an expedition to the moon's northern pole. It would launch from Cape Canaveral atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 launch vehicle. The company, in partnership with CMU, seeks to win the Google Lunar X Prize of more than $20 million.
Polaris is a flight prototype but has the same configuration as the rover that will eventually land on the moon. This will enable Astrobotic team members to spend the coming months testing and improving the robot's computer vision, navigation, and planning software, and software that can plot the rover's position on the moon within 10 ft. It includes a number of flight-worthy components, including wheels and chassis beams constructed of light, but tough, composite materials.
"It is the first rover developed specifically for drilling lunar ice," says William 'Red' Whittaker, Astrobotic CEO and founder of the Field Robotics Center at CMU's Robotics Institute. Other robots built by the Field Robotics Center have developed technologies necessary for lunar drilling, but none of those machines was ever meant to leave Earth. "What Polaris does is bring those many ideas together into a rover configuration that is capable of going to the moon to find ice," he says.
Observations by NASA and Indian spacecraft suggest that a substantial amount of water ice could exist at the lunar poles. That ice could be a source of water, fuel, and oxygen for future expeditions.
To find the ice, a rover must operate as close to the dark poles as possible, but not so far that it can't use solar arrays for power, Whittaker says. So Polaris has three large solar arrays, arranged vertically, to capture light from low on the horizon. The solar arrays will be capable of an average of 250 W of electrical power.
Polaris also makes use of software, pioneered in CMU's NASA-funded Hyperion robot, that keeps track of the rover's position relative to the sun's rays to maximize solar energy and husbands battery power for use in the long shadows and dark regions found at the poles.
Polaris, 5 1/2 ft tall, 7 ft wide, and almost 8 ft long, can move at about 1 ft/sec on 2-ft-diameter composite wheels. Like Scarab, a NASA-funded robot built by CMU, its suspension will enable the rover to rise up over rough terrain, but also lower itself to the ground to perform drilling. The rover will weigh 150 kg, or about 330 lb, and can accommodate a drill and science payload up to 70 kg, or a bit more than 150 lb.
"The composite materials are of aerospace quality, and that's a huge step up for us," Whittaker says. The lighter structural materials are essential for Polaris to accommodate the heavy drill as well as the massive batteries it will need for low-light operations. The carbon fiber and Kevlar materials also are important to the mission because they won't release gases in the moon's hard vacuum. The robot's science package will include gas sensors that could be disrupted by such out-gasing, he explains.
Whittaker says the lunar day lasts about 14 Earth days, though only about 10 days are suitable for water prospecting at the poles. The Astrobotic team expects Polaris could drill 10 to 100 holes during that time as it locates and characterizes water ice deposits. But if Polaris successfully survives the long, frigid lunar nights, as anticipated, the prospecting mission could be extended indefinitely.
Astrobotic has won nine lunar contracts from NASA worth $3.6 million, including one to evaluate how Polaris can accommodate NASA's ice-prospecting instruments during a three-mile traverse near the moon's north pole.
Astrobotic earlier developed a robot called Red Rover suitable for equatorial destinations. The design of Polaris is significantly different, reorienting the solar arrays to capture tangential light, rather than the overhead light of equatorial regions. It also is larger and generates more power to operate the science package. Griffin, a lunar landing vehicle being developed by Astrobotic, can accommodate either rover.
Source: Carnegie Mellon University
Published October 2012
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy